Understanding The Hydrosphere: A Comprehensive Explanation
The hydrosphere is an essential component of the Earth, encompassing all forms of water found on our planet. From the vast oceans and seas to the smallest droplets of moisture in the atmosphere, the hydrosphere plays a crucial role in maintaining life and shaping the environment. It is not just about the water we see; it includes glaciers, rivers, lakes, groundwater, and even water vapor. This interconnected system influences climate patterns, supports ecosystems, and is vital for human existence.
Throughout history, the hydrosphere has been a focal point of study for scientists, environmentalists, and geographers alike. Understanding the hydrosphere is key to addressing pressing global issues such as climate change, water scarcity, and pollution. By exploring its various components and functions, we can better appreciate the intricate balance that sustains life on Earth.
In this article, we will delve into the explanation of the hydrosphere, examining its various forms, functions, and significance. We will also address frequently asked questions about this vital Earth system, providing insights that are essential for anyone interested in environmental science or simply curious about our planet's water resources.
What is the Hydrosphere?
The hydrosphere refers to all the water found on, under, and above the surface of the Earth. This includes:
- Ocean water
- Glaciers and ice caps
- Groundwater
- Rivers and lakes
- Atmospheric water vapor
Collectively, these components make the hydrosphere a dynamic and ever-changing part of the Earth’s system, interacting with the lithosphere (land), biosphere (life), and atmosphere (air) in complex ways.
How Does the Hydrosphere Interact with Other Spheres?
The hydrosphere interacts with the lithosphere, biosphere, and atmosphere in several significant ways:
- Water erosion shapes landforms and landscapes.
- Water is essential for all living organisms, supporting biodiversity.
- The atmosphere influences water distribution through precipitation and evaporation.
This interplay is crucial for maintaining the planet’s ecological balance, influencing everything from weather patterns to the availability of freshwater resources.
Why is the Hydrosphere Important for Life on Earth?
The hydrosphere is vital for life for numerous reasons:
- It provides drinking water for humans and animals.
- It supports agriculture through irrigation.
- It regulates climate and temperature.
- It is home to diverse aquatic ecosystems.
Without the hydrosphere, life as we know it would not exist. It sustains ecosystems, influences weather, and is integral to human health and well-being.
What Are the Different Forms of Water in the Hydrosphere?
The hydrosphere comprises various forms of water, which can be classified into categories based on their state and location:
- Liquid Water: Found in oceans, rivers, lakes, and groundwater.
- Solid Water: Present as ice in glaciers and ice caps.
- Gaseous Water: Exists as water vapor in the atmosphere.
This variety enables the hydrosphere to play multiple roles in Earth’s processes, from weather phenomena to geological transformations.
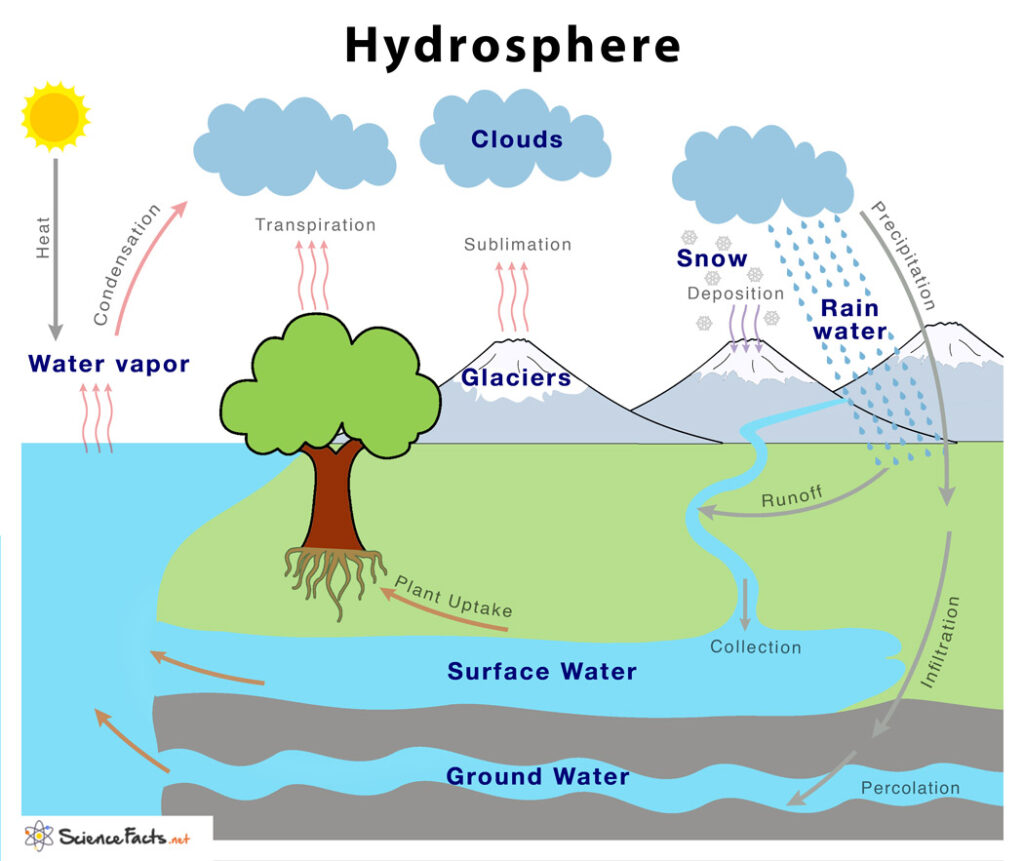
How Does Water Cycle Through the Hydrosphere?
The water cycle is a fundamental process that circulates water within the hydrosphere. It includes the following stages:
This cycle is vital for replenishing water resources, supporting agriculture, and maintaining ecosystems.
What Impact Does Climate Change Have on the Hydrosphere?
Climate change poses significant threats to the hydrosphere, influencing water availability, quality, and distribution. Key impacts include:
- Increased evaporation leading to drier conditions.
- Melting glaciers contributing to rising sea levels.
- Altered precipitation patterns resulting in floods or droughts.
- Ocean acidification affecting marine life.
Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate risks and protect our water resources.
How Can We Protect the Hydrosphere?
Protecting the hydrosphere is essential for ensuring a sustainable future. Here are some strategies:
- Conserving water through responsible usage.
- Reducing pollution by properly disposing of waste.
- Restoring wetlands and riparian zones.
- Advocating for policies that protect water resources.
By taking these actions, individuals and communities can help safeguard the hydrosphere and its vital contributions to life on Earth.
Conclusion: The Significance of Understanding the Hydrosphere
The explanation of the hydrosphere highlights its critical role in sustaining life, regulating climate, and influencing geological processes. As we face challenges such as climate change and water scarcity, understanding the hydrosphere becomes increasingly important. By fostering awareness and taking action to protect our water resources, we can ensure a healthier planet for future generations.


ncG1vNJzZmixn6PAtr7IZqWeq6RjsLC5jq2pnqaUnruogY6er6mkkaOutbXOp2Sonl2dxqW%2BzqynoZ2imnupwMyl