Understanding The Circular Flow Of Income: Answers To Your Questions
The concept of the circular flow of income is pivotal in understanding how economies operate. It describes the continuous movement of money among different sectors of the economy, illustrating the interconnectedness of producers and consumers. This model is essential for grasping how economic stability is achieved and maintained. The circular flow highlights the exchanges that occur in an economy, helping individuals and businesses understand their roles within the larger economic system. As such, it is fundamental to both economic theory and practical applications.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the circular flow of income, breaking down answers to common questions that emerge around this crucial economic model. By exploring these queries, we aim to provide clarity and insight into how income circulates within an economy, affecting everything from production to consumption. Whether you are a student, a professional in the field, or simply someone looking to understand economic principles better, this exploration will equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate economic discussions.
As we answer these questions, we will not only clarify the concept of the circular flow of income but also highlight its relevance in today's economy. Understanding this flow is crucial for anyone looking to comprehend the dynamics of economic interactions and the impact of policy decisions. Join us as we unravel the complexities of the circular flow of income to the questions you just answered.
What is the Circular Flow of Income?
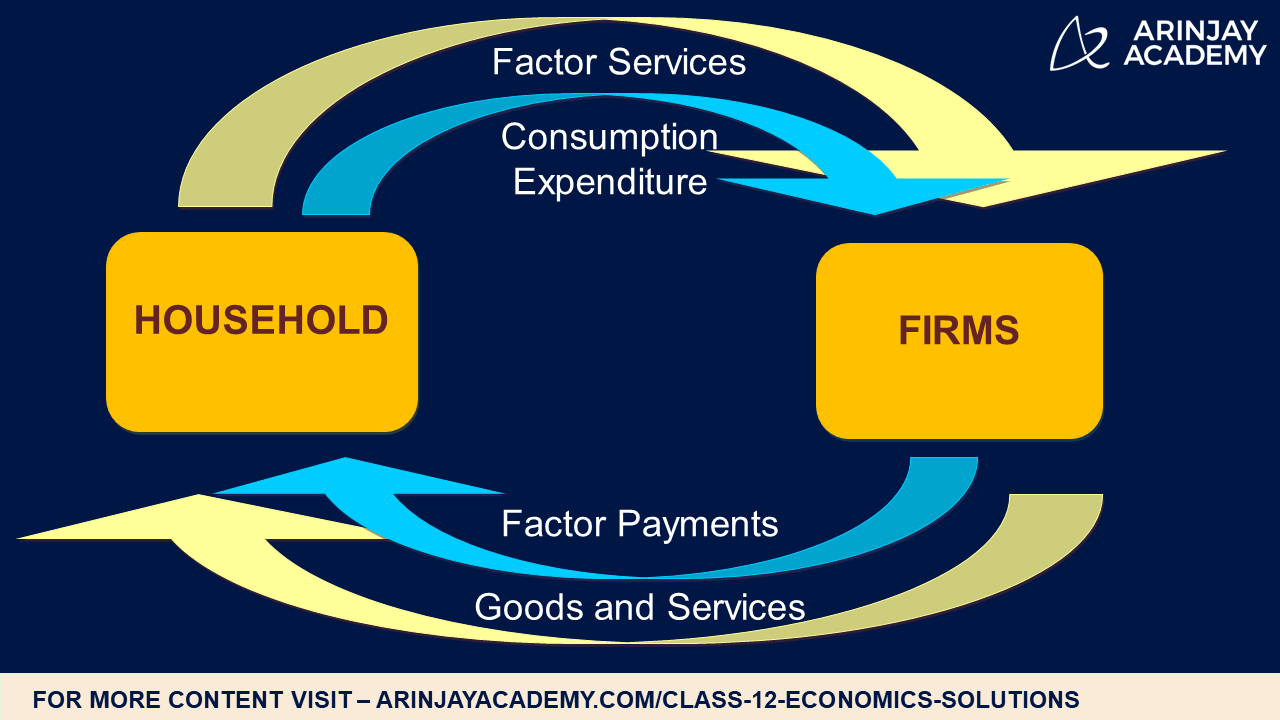
The circular flow of income is an economic model that illustrates how money moves through different sectors of the economy. At its core, it demonstrates the interactions between households and businesses, showing how income is generated, spent, and re-circulated.
How Does the Circular Flow of Income Work?
The circular flow operates through a series of transactions between two main sectors: households and firms. Households provide factors of production—such as labor, land, and capital—to firms, which in turn produce goods and services. The flow of income occurs as firms pay wages and rents to households for these factors. This income is then used by households to purchase goods and services from firms, completing the cycle.
What Are the Key Components of the Circular Flow Model?
- Households: These are consumers who provide labor and resources.
- Firms: These are producers of goods and services.
- Government: The government can influence the flow through taxation and spending.
- Financial Institutions: Banks and other institutions facilitate savings and investments.
What Role Does Government Play in the Circular Flow of Income?
Government plays a crucial role in the circular flow of income by regulating economic activity and providing public goods and services. Through taxation, the government collects revenue from households and firms, which is then redistributed through public spending on infrastructure, education, and social services. This interaction creates additional flows of income within the economy.
How Do Leakages and Injections Affect the Circular Flow of Income?
In the circular flow of income, leakages (such as savings, taxes, and imports) and injections (like investments, government spending, and exports) significantly impact the economy's overall health. Leakages reduce the amount of money circulating within the economy, while injections increase it, helping to maintain equilibrium.
Can You Explain the Importance of the Circular Flow of Income to Economic Stability?
The circular flow of income is vital for economic stability as it illustrates how income is generated and spent. A balanced flow ensures that all sectors of the economy can thrive, leading to sustained growth. Disruptions in this flow can lead to unemployment, reduced consumer spending, and economic downturns.
What Are the Real-World Implications of Understanding the Circular Flow of Income?
Grasping the circular flow of income helps policymakers, businesses, and individuals make informed decisions. For instance, understanding how changes in taxation or government spending can influence economic activity allows for better policy-making. Similarly, businesses can strategize their operations based on consumer spending patterns.
How Can the Circular Flow of Income Be Applied to Current Economic Events?
Understanding the circular flow of income enables economists and analysts to assess the impact of recent economic events, such as stimulus packages or market disruptions. By analyzing these flows, stakeholders can predict how various sectors will respond, allowing for proactive measures to mitigate negative effects.
What Future Trends Can We Expect in the Circular Flow of Income?
As economies evolve, so too does the circular flow of income. Emerging trends, such as digital currencies and the gig economy, are reshaping how income circulates. Observing these changes is essential to understanding future economic landscapes and preparing for shifts in consumer behavior.


ncG1vNJzZmixn6PAtr7IZqWeq6RjsLC5jq2pnqaUnruogY6coKubpaGus3nFpaawZZ%2Bbeqq6wqiknmWkpHq1tMRmqK6do6m2sLrSZrCorV2fwrTAjJqlrK%2BVp7KlecinZLKnpad7qcDMpQ%3D%3D