UN Human Development Index, 2009 And Its Depiction
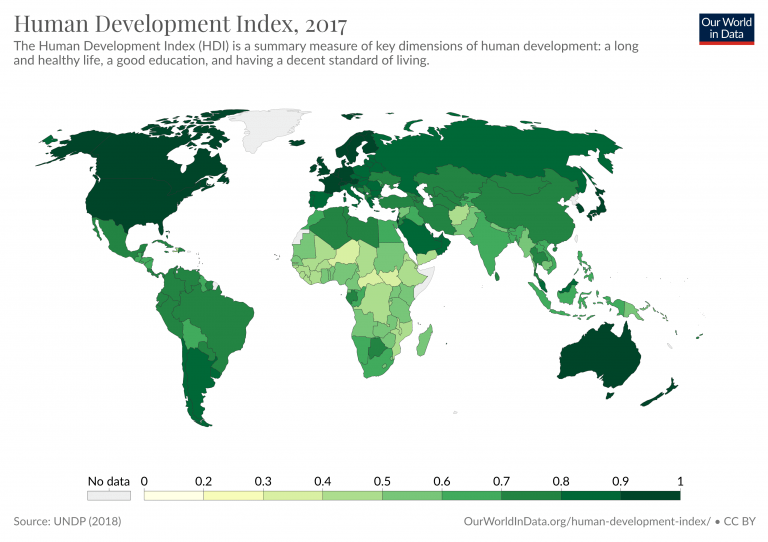
The UN Human Development Index (HDI) serves as a powerful tool for assessing the well-being and development of nations around the globe. The year 2009 marked a pivotal moment in the analysis of human development, with the release of various maps that visually represented the HDI across different countries. These maps not only highlighted disparities in health, education, and income but also sparked conversations about global inequalities and development priorities. The maps above serve as a visual narrative, illustrating how countries are positioned on the development spectrum and prompting us to consider the underlying factors contributing to these differences.
In examining Map 2: UN Human Development Index, 2009, we can discern significant trends and patterns that reveal the complex relationship between economic growth and human welfare. Countries are often categorized into different tiers based on their HDI scores, which reflect their achievements in areas such as life expectancy, education levels, and per capita income. By analyzing these maps, we can gain valuable insights into the challenges faced by lower-ranked nations and the success stories of those that have excelled in promoting human development.
As we delve deeper into the maps above, we will explore the implications of the HDI in understanding global development. How do these maps inform policy decisions? What can be learned from the comparative analysis of different countries? By answering these questions, we can better appreciate the significance of the UN Human Development Index and its role in shaping a more equitable world.
What is the UN Human Development Index?
The UN Human Development Index (HDI) is a composite measure that evaluates and ranks countries based on three key dimensions:
- Health: Measured by life expectancy at birth.
- Education: Assessed through mean years of schooling and expected years of schooling.
- Standard of Living: Evaluated using Gross National Income (GNI) per capita.
This multi-dimensional approach allows for a more comprehensive understanding of human development compared to purely economic indicators.
How Does Map 2: UN Human Development Index, 2009 Depict Global Development?
Map 2 offers a visual representation of the HDI scores across various countries, effectively categorizing them into distinct groups:
- High Human Development: Countries with HDI scores above 0.8.
- Medium Human Development: Those falling between 0.5 and 0.799.
- Low Human Development: Nations with scores below 0.5.
This classification not only highlights the disparity in development but also serves as a call to action for policymakers and global leaders.
What Trends Can Be Identified in Map 2?
Upon examining the map, several notable trends emerge:
- Regions such as Western Europe and North America predominantly fall into the high HDI category.
- Many countries in Sub-Saharan Africa are marked with low HDI scores.
- Emerging economies in Asia and Latin America show a mix of medium and high HDI classifications.
These trends reflect historical, social, and economic contexts that have shaped each region's development trajectory.
What Factors Contribute to Variations in HDI Scores?
The variations in HDI scores across countries can be attributed to several interrelated factors:
- Economic Stability: Countries with robust economies often provide better services and opportunities for their citizens.
- Access to Education: Education plays a crucial role in enhancing life chances and contributing to higher HDI scores.
- Healthcare Systems: Effective healthcare systems improve life expectancy and overall well-being.
Understanding these factors allows stakeholders to develop targeted strategies aimed at improving human development.
How Can Map 2 Influence Policy Decisions?
Map 2: UN Human Development Index, 2009 has significant implications for global policy and development strategies:
- Policymakers can identify regions in need of immediate attention and resources.
- International aid organizations can tailor their programs to address specific challenges faced by low HDI countries.
- Governments can use HDI data to set realistic development goals and measure progress over time.
By leveraging the insights provided by the map, stakeholders can work collaboratively towards improving human development outcomes.
What Lessons Can Be Learned from the 2009 HDI Maps?
The maps from 2009 serve as a historical benchmark, allowing us to reflect on progress and setbacks in human development:
- The importance of sustained investment in education and healthcare.
- The necessity of addressing economic inequalities within and between nations.
- The role of international cooperation in tackling global challenges.
These lessons continue to resonate as we navigate the complexities of development in the 21st century.
What Future Trends May Emerge in Human Development?
As we look ahead, several trends may shape the future of human development:
- Technological Advancements: The rise of technology could enhance access to education and healthcare.
- Climate Change: Environmental challenges may exacerbate existing disparities in HDI scores.
- Global Pandemics: Public health crises can have lasting impacts on nations' development trajectories.
Continuing to monitor these trends through the lens of the HDI will be essential in guiding future efforts towards equitable development.
Conclusion: The Significance of Map 2 in Understanding Human Development
In summary, Map 2: UN Human Development Index, 2009 plays a vital role in depicting global development disparities and informing policy decisions. By understanding the factors that contribute to variations in HDI scores and the lessons learned from historical data, we can work towards a more equitable and just world. The insights garnered from the maps above are pivotal in shaping future strategies aimed at improving human well-being and development outcomes for all nations.


ncG1vNJzZmixn6PAtr7IZqWeq6RjsLC5jq2pnqaUnruogY6mmKllYmLCr3nHrqSapl2Zsrexy6inpp2eqXqqusOer2ZqYGWGbrHXqaOaoZ5itbDDjK2fnmWdlr20ecCbpq%2BdXZmysbXCrWWhrJ2h