Exploring The Shrinking Coastal Areas Of Our Continents
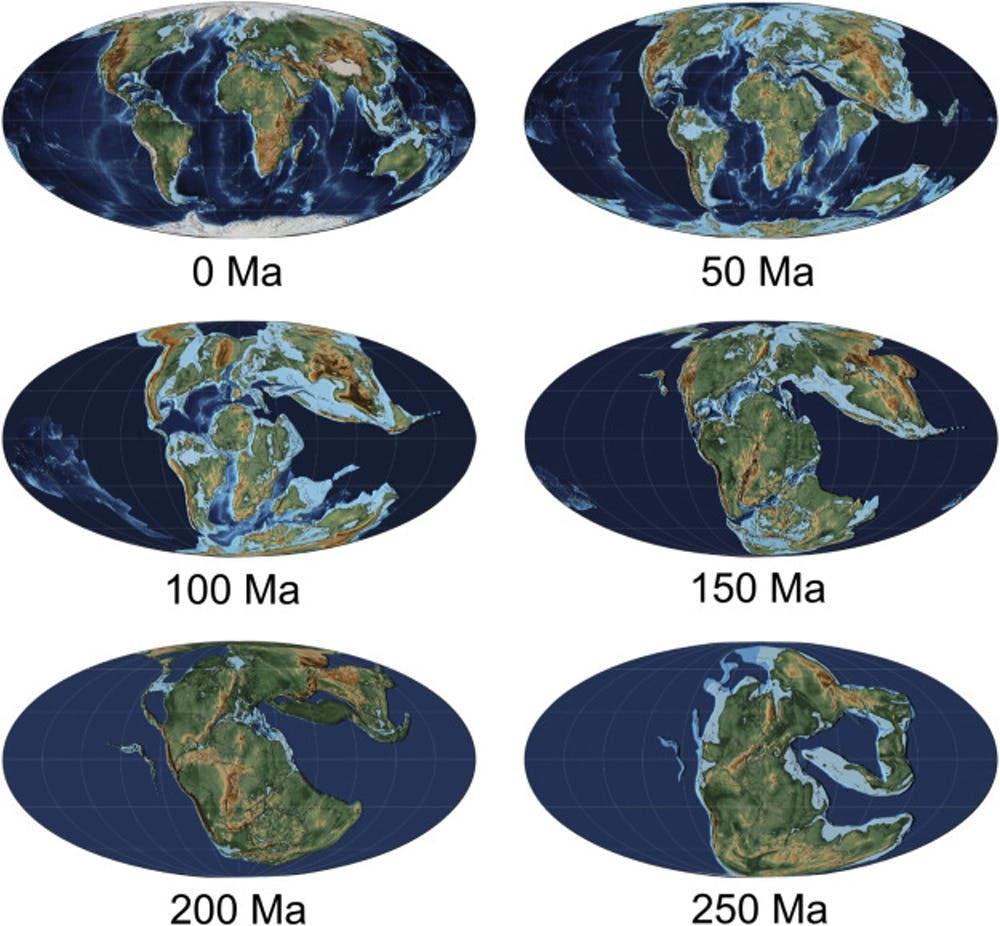
Millions of years ago, our planet was a vastly different place, teeming with extensive coastlines and diverse marine ecosystems. Today, the scenarios have drastically changed, revealing a striking truth: continents have fewer coastal areas than they did millions of years. As geological processes continue to reshape our planet, understanding the implications of these changes becomes increasingly crucial. This article delves into the fascinating history and evolution of coastal areas, exploring how and why these transformations have occurred.
Coastal regions have long been revered for their ecological significance and economic value. They serve as vital habitats for countless species, provide resources for human communities, and act as buffers against the forces of nature. However, various factors, including tectonic shifts, climate changes, and human activities, have led to the gradual erosion of these coastal areas. Did you know that some regions that were once bustling with marine life have now become arid land? The changes aren’t just geological; they have profound implications for biodiversity and human settlement.
As we explore the reasons behind the dramatic reduction in coastal areas over millions of years, it’s essential to appreciate the intricate relationship between land and sea. This article will take you through the geological processes that have shaped our continents, the impact of climate change, and the future of coastal ecosystems. Join us on this journey to understand the fascinating yet alarming reality that continents have fewer coastal areas than they did millions of years ago.
What Geological Processes Have Led to Changes in Coastal Areas?
To understand why continents have fewer coastal areas than they did millions of years ago, we must first look at the geological processes at play. The Earth's crust is in a constant state of flux, with tectonic plates shifting and reshaping the landscape. Here are some key processes that have contributed to the transformation of coastlines:
- Plate Tectonics: The movement of tectonic plates can cause land to rise or sink, directly affecting coastal geography.
- Sea Level Changes: Fluctuations in sea levels, due to melting ice caps or changes in ocean temperatures, can lead to the flooding of coastal areas or the exposure of land.
- Erosion and Sedimentation: Natural processes such as wave action, currents, and wind contribute to the erosion of coastlines, while sedimentation can build new landforms.
- Volcanic Activity: Volcanic eruptions can create new land but can also alter existing coastal areas dramatically.
How Has Climate Change Impacted Coastal Areas?
The impact of climate change on coastal areas is profound and multifaceted. Rising global temperatures have led to significant changes in climate patterns, resulting in the following effects:
- Melting Ice Caps: The melting of polar ice caps contributes to rising sea levels, which can inundate coastal areas.
- Changing Weather Patterns: Increased frequency and intensity of storms can lead to coastal erosion and habitat destruction.
- Ocean Acidification: Higher carbon dioxide levels result in ocean acidification, affecting marine life and ecosystems.
What Are the Implications of Fewer Coastal Areas for Biodiversity?
As continents have fewer coastal areas than they did millions of years ago, the implications for biodiversity are significant. Coastal ecosystems, such as mangroves, estuaries, and coral reefs, are rich in biodiversity. The reduction of these areas can lead to:
- Loss of Habitat: Many species rely on coastal habitats for breeding, feeding, and shelter. Their loss can lead to population declines and extinction.
- Disruption of Food Chains: The interconnectedness of ecosystems means that the decline of one species can have cascading effects on others.
- Increased Vulnerability: Reduced coastal areas can lead to diminished resilience against climate change impacts, making ecosystems more susceptible to further degradation.
What Role Do Humans Play in the Reduction of Coastal Areas?
Human activities have significantly accelerated the reduction of coastal areas. As populations grow and urbanization expands, various factors come into play:
- Urban Development: Coastal areas are often prime locations for cities and industries, leading to habitat destruction and land reclamation.
- Pollution: Coastal pollution from agriculture, industry, and urban runoff can harm marine life and degrade ecosystems.
- Deforestation: The removal of mangroves and other coastal vegetation can lead to increased erosion and loss of protective barriers.
What Can Be Done to Protect Remaining Coastal Areas?
As the reality that continents have fewer coastal areas than they did millions of years becomes more evident, proactive measures are necessary to protect what remains. Here are some strategies:
- Conservation Efforts: Establishing protected marine areas can help safeguard critical habitats and promote biodiversity.
- Restoration Projects: Initiatives to restore degraded coastal areas, such as replanting mangroves, can enhance resilience against climate change.
- Sustainable Development: Balancing development with environmental protection is crucial for maintaining healthy coastal ecosystems.
How Can Individuals Contribute to Coastal Conservation?
While large-scale efforts are essential, individual actions can also make a difference. Here are some ways to contribute to coastal conservation:
- Educate Yourself and Others: Understanding the importance of coastal ecosystems can foster a sense of responsibility.
- Reduce Plastic Usage: Minimizing plastic consumption helps reduce marine pollution.
- Participate in Clean-Up Events: Joining local initiatives to clean up beaches and coastal areas can have a positive impact.
Conclusion: The Future of Our Coastal Areas
In conclusion, the fact that continents have fewer coastal areas than they did millions of years ago serves as a reminder of the dynamic nature of our planet and the pressing need for conservation. As we navigate the challenges posed by climate change and human activities, it is imperative to adopt sustainable practices that protect our coastal ecosystems. By increasing awareness, supporting conservation initiatives, and taking individual action, we can work together to preserve these vital areas for future generations. The journey toward protecting our coasts is ongoing, but every effort counts in ensuring that these magnificent ecosystems continue to thrive.

ncG1vNJzZmixn6PAtr7IZqWeq6RjsLC5jq2pnqaUnruogY6cpqesmaOyr8DSZp%2BarpVis6bDxKtknKeRqMGiuIyaqZ6Zo2LBqa3NZquhnalisaqwjKagpaSZpLu0ec6fZLKdkafAb7TTpqM%3D